
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is NASA’s next flagship Astronomy and Astrophysics space observatory, following the Hubble and James Webb Space Telescopes (HST and JWST). Launch of Roman is planned for 2027. Whereas HST and JWST focus on small regions of the universe with narrow field of view instruments, the Roman Space Telescope has a wide field of view, 100 times the field of view of Hubble. Roman’s wide field of view, combined with the light gathering power of a 2.4-meter primary mirror, will settle essential questions in the areas of dark energy, exoplanets, and infrared astrophysics. Roman will survey billions of galaxies and study thousands of exoplanets.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20211208005098/en/
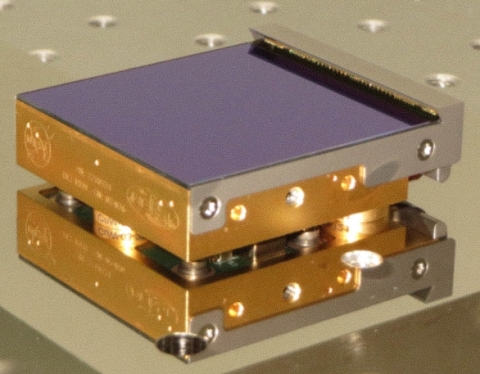
The 16.7 million pixel H4RG-10 sensor chip assembly (SCA) is shown in the photo. Image credit: NASA / Goddard Spaceflight Center
Roman’s wide field of view required a new generation of infrared detector developed by Teledyne Imaging Sensors in Camarillo, California. The infrared sensor chip assembly (SCA) developed for Roman is the H4RG-10, 4,096 by 4,096 pixels, each pixel is 10 by 10 microns in size. (A human hair is about 100 microns wide.) Eighteen (18) H4RG-10 SCAs are in the focal plane mosaic of Roman, totalling over 300 million pixels. This is by far the largest infrared focal plane ever made, for space or ground-based facilities.
Teledyne was awarded a $23 million contract in 2018 to supply 24 flight quality SCAs; 18 for flight and 6 flight spares. Teledyne achieved a high level of contract execution:
- 28 flight quality SCAs have been delivered (4 more than required).
- All 28 SCAs exceed the specifications for quantum efficiency (ability to detect photons), low noise (dark current, readout noise), and very low image persistence (also known as image lag or memory effect).
- The ability of Teledyne’s infrared detectors to also detect visible wavelengths has enabled Roman’s wide field of view instrument to increase the spectral bandwidth by 20%.
- Teledyne continued working throughout the pandemic, ensuring the infrared detectors were delivered before the dates needed for the Wide Field Instrument.
In addition to the infrared arrays, Teledyne is producing the visible light detectors that will be used in the coronograph instrument of the Roman Space Telescope.
“Teledyne is proud to provide the high performance infrared detectors for the Roman Space Telescope,” said Dr. John Auyeung, Teledyne’s Director of Astronomy & Earth Observation and Program Manager for Roman SCA development and flight production. “I have been fortunate to serve as the program manager for the infrared arrays supplied to Hubble, JWST, and Roman. The partnership with Goddard Spaceflight Center has been the highlight of my career.”
About Teledyne Technologies
Teledyne Technologies is a leading provider of sophisticated digital imaging products and software, instrumentation, aerospace and defense electronics, and engineered systems. Teledyne’s operations are primarily located in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Western and Northern Europe. For more information, visit Teledyne’s website at www.teledyne.com.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20211208005098/en/
Contacts:
(805) 373-4542


